
Establishing and working within tolerances is essential for maintaining product functionality, uniformity and aesthetics. Without tolerances, manufacturers compromise their product’s quality — and their revenue. As such, manufacturers must prioritize systems and solutions that ensure high-quality products.
Vacuum coating is an internal manufacturing process that helps protect product surfaces from water, weather, corrosion and other damage. It’s also a method for minimizing errors and ensuring consistently high-quality products.
Vacuum coating is an excellent method of creating thin protective layers on object surfaces. With vacuum coating systems, manufacturers can apply an even coating on surface substrates for improved durability, efficiency, functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Vacuum coating or film deposition is applying a thin coating layer to substrate surfaces like medical equipment to protect it from wear. It works through a vacuum chamber process that transfers atoms or molecules to the product’s surface.
You can use vacuum coating technology for applications like car and aerospace components. These coatings can prevent water and heat damage and other deterioration of equipment and products. You can also use various types of coatings applied via vacuum deposition chamber depending on the industry and the product requirements. Different vacuum or deposition coatings provide equipment and products with unique finishes and protection levels.
Understanding the meaning of vacuum coating begins with identifying different coating techniques.
Physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a common coating technique used in various industries. It uses a vacuum deposition chamber process that vaporizes a solid metallic material. The vaporized metal or atoms then penetrate the product’s surface and form a protective layer or coating.
The coating becomes an integral part of the surface, creating an impenetrable layer around the components. PVD coating provides products with a protective layer that will not crack or peel. Manufacturers rotate products while in the chamber to ensure they develop an even coat. PVD coating can be performed via different methods, including sputtering and cathodic arc:
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) coating uses hydrogen to transfer a chemical vapor onto a substrate’s surface. The chemicals are moved and deposited onto an object through thermal activation.
The chemical vapors break down and then collect on the substrate’s surface to create compounds like nitrides. You can also use plasma to enhance the extraction and coating process. Plasma allows chemical breakdown and deposition to happen at lower temperatures.
Thermal evaporation is a traditional coating method that transfers vapor onto a substrate. Here, metal material is melted, vaporized at high temperatures and deposited onto an object to create a thin coating. You can use various thermal evaporators to accomplish this process, such as tungsten wires and electron beams.
Manufacturers can use thermal evaporation for coating and enhancing optic lenses. Coating optic lenses can improve protection against ultraviolet light. Manufacturers can also use thermal evaporators to create aluminum film layers in consumer product packaging such as chip packets. The coating or film prevents air and moisture from entering the packaging.
A vacuum coating system has numerous parts, each of which plays a vital role in coating a substrate. The following are some definitions of vacuum coating components:
A vacuum chamber is used for holding and protecting a workpiece during the coating process. To begin coating, you must place a workpiece into a clean, empty chamber. The vacuum chamber vaporizes and transfers materials onto the substrate while maintaining a contaminant-free environment to ensure successful coating application. A PVD vacuum coating machine may require repositioning and rotating an object in the chamber for sufficient coating.
Vacuum machine pumps create suction in the chamber for extracting and transferring materials onto an object. Vacuum deposition equipment may use various types of pump systems, such as cryogenic, turbomolecular or diffusion options.
Thermal evaporation systems have numerous evaporators, like wires and electron beams. Heating wires electrically or coating them in a metal container that has a high melting point creates vapor. The chemical vapor is suctioned by pumps in the vacuum chamber and transferred onto a workpiece. You can also use an electrical beam to melt metal materials, creating high evaporation rates.

Industries use vacuum coating in multiple applications, including the production of manufacturing tools and automotive, aerospace and medical components. The following are a few common uses for coatings in these sectors:
Automotive industries vacuum coat parts like engines, steering columns, and interior and exterior car components. Coatings enhance car components’ aesthetics, functionality and durability. Vacuum coating can also help protect brakes from overheating, corrosion and deterioration.
Aerospace components must work under extreme conditions while subject to factors like high heat and the elements. Vacuum coating protects aerospace equipment at high speeds and altitudes from heat damage and friction.
Vacuum coating is excellent for protecting tools from wear and damage. It helps reinforce cutting edges while maintaining their ability to hold tolerances. The right coating will provide a protective layer that imparts tools with enhanced characteristics like heat and friction resistance to improve their performance and longevity.
Vacuum coating is used for various medical tools like dental and surgical instruments. Coating medical devices can enhance their antimicrobial properties while reducing the likelihood of allergic reactions to chemicals like nickel. It also reduces friction and improves aesthetics.
Vacuum coating is often used to create durable furniture and decorative finishes. Manufacturers can use it for coating hardware like door knobs and kitchen and bathroom faucets. Vacuum coating can also enhance the aesthetics and durability of jewelry and watches.

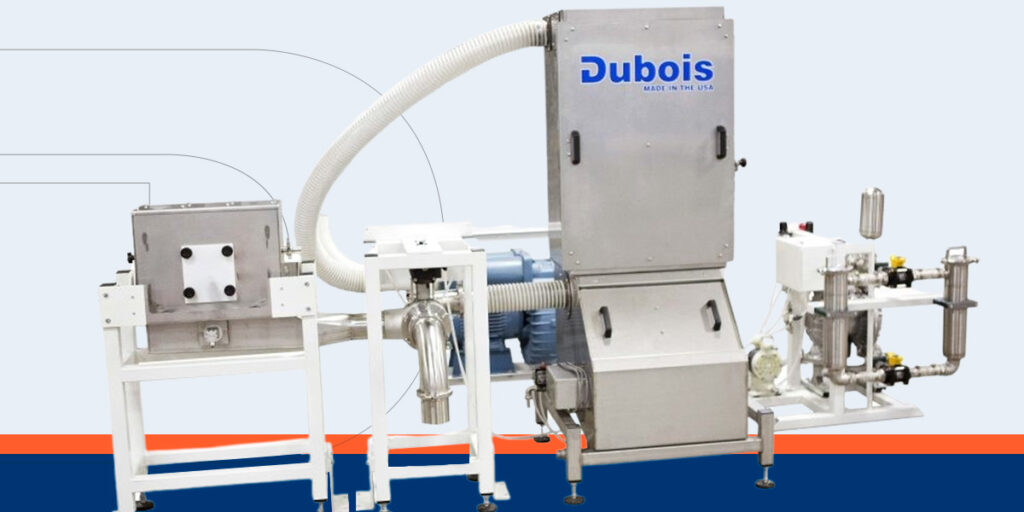
At Dubois Equipment, we offer quality vacuum coating systems and solutions for protecting and finishing components. We focus on understanding our customers’ needs to provide precise machine integrations that work for their specific purposes.
With our years of industry experience, we know how to deliver customized solutions for your applications. In partnership with Timesavers, we provide quick turnaround times on machines to ensure you have everything you need to maximize your productivity.
Contact us online for a quote or reach out to a Dubois representative to learn more about our vacuum coating systems and solutions.